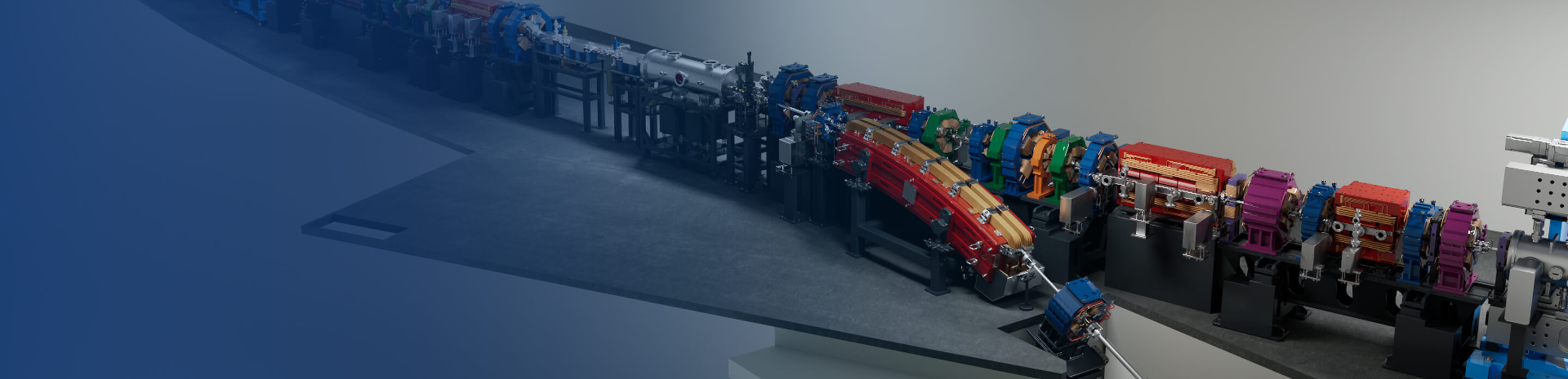
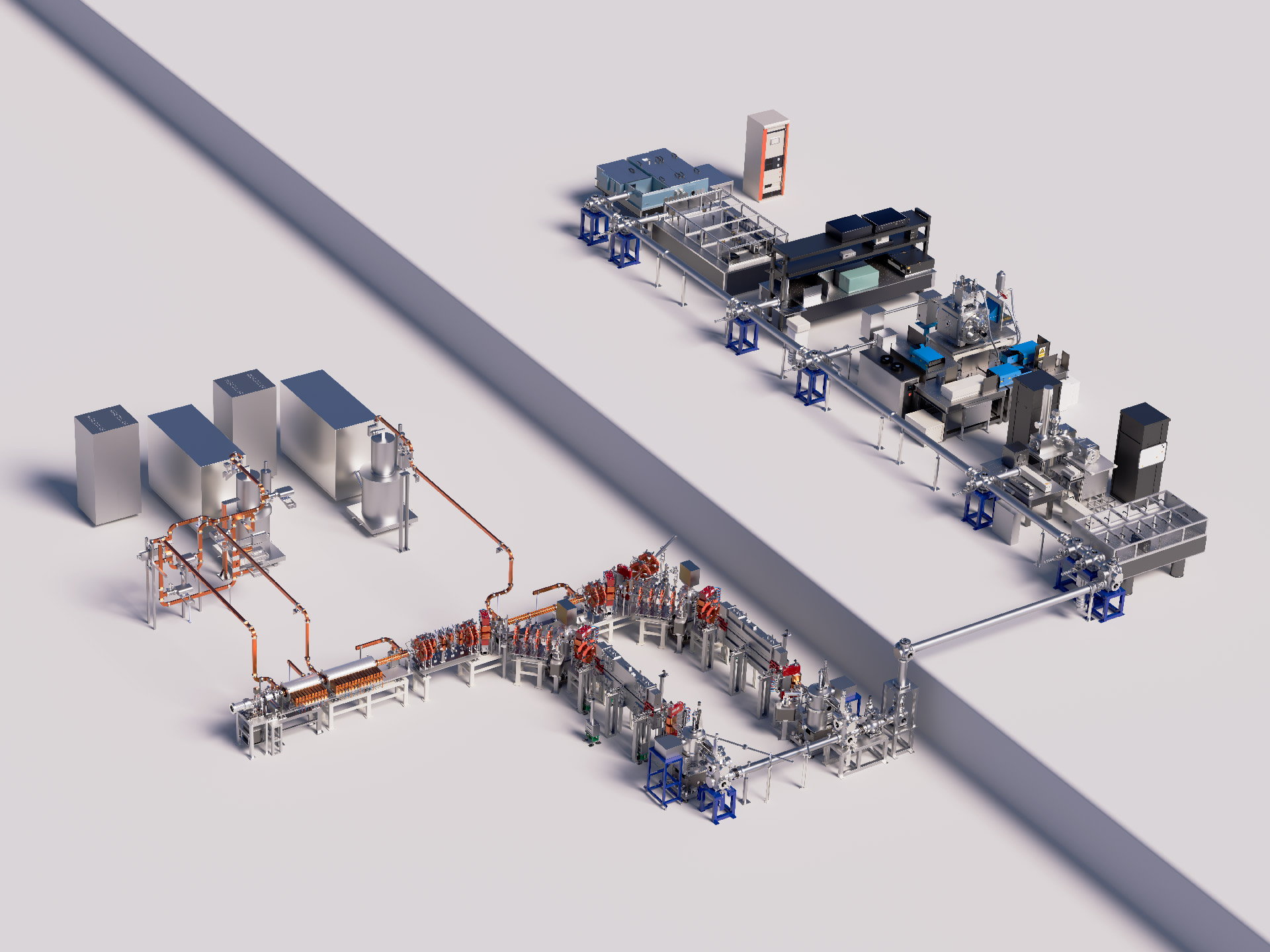
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a powerful coherent radiation source generated using free electrons in a vacuum as the working medium. It exhibits outstanding advantages such as high power, broadband continuous tunability, and short pulse duration. FELs can cover wavelengths from terahertz to hard X-rays and are widely applied in fundamental research areas including condensed matter physics, advanced materials and surface physics, atomic and molecular physics, chemistry, and biology.
FELiChEM
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a powerful coherent radiation source generated using free electrons in a vacuum as the working medium. It exhibits outstanding advantages such as high power, broadband continuous tunability, and short pulse duration. FELs can cover wavelengths from terahertz to hard X-rays and are widely applied in fundamental research areas including condensed matter physics, advanced materials and surface physics, atomic and molecular physics, chemistry, and biology. They have also driven significant technological innovations in strategic security, aerospace, energy and environmental sciences, medicine, chemical engineering, and advanced manufacturing.
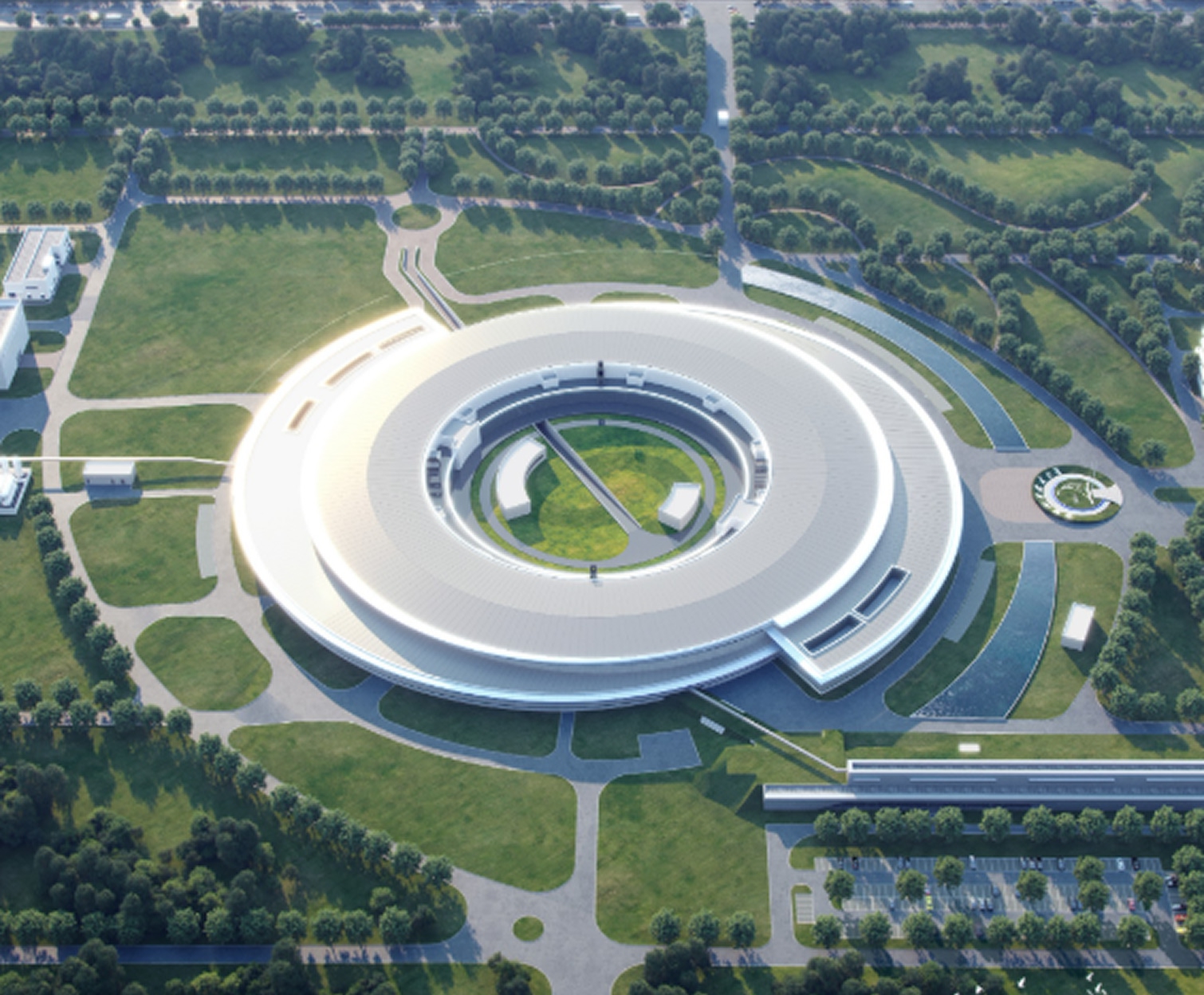
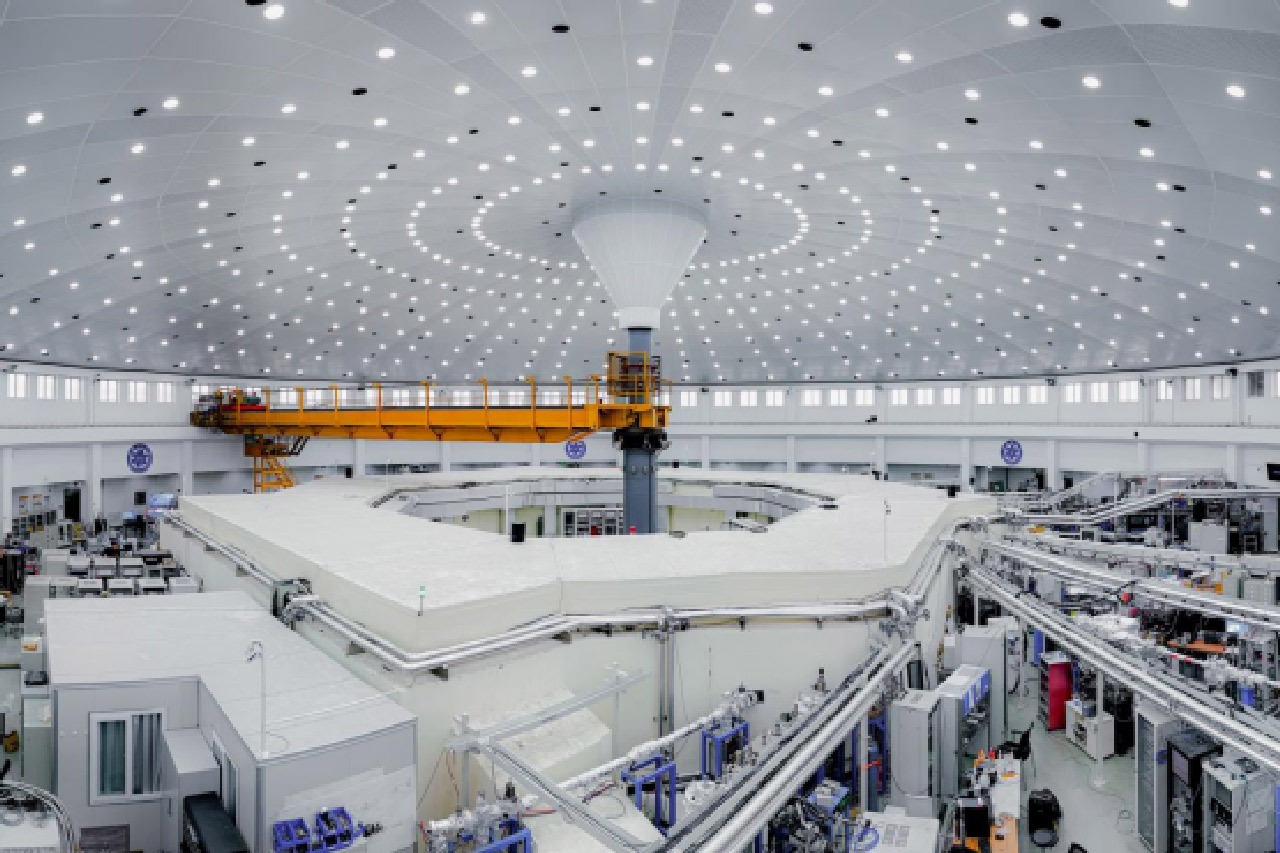
The Hefei Infrared Free-Electron Laser—"Tunable InfreRed Laser for Fundamentals of Energy Chemistry"—was jointly constructed by Xiamen University, the University of Science and Technology of China, Fudan University, and the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. It passed national acceptance in March 2022. As China’s first user-oriented FEL facility covering mid- to far-infrared wavelengths, this facility is also the world’s first infrared free-electron laser facility dedicated to energy chemistry research.
The Hefei Infrared Free-Electron Laser facility comprises five experimental beamlines: photodissociation spectroscopy, photoexcitation spectroscopy, sum-frequency generation spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy-infrared spectroscopy, and surface/interface reflection-absorption infrared spectroscopy stations.