Imaging research
The progress of high resolution X-ray imaging in cell imaging research
Microscopy plays an important role in the research of some major issues in life science. In recent decades, high-resolution X-ray imaging has been rapid development. Due to the stronger penetrability, high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray imaging technology is becoming an advanced tool for the study of cells than the common tools such as optical microscopy and electron microscopy. It can image cell samples at the cellular level with non-destructive (not sliced), high resolution (several tens of nanometers) and the natural state (using phase contrast). These conditions could not be observed by optical microscopy and electron microscopy. Moreover, integrating with computed tomography (CT), three-dimensional internal structure of the cells can be also observed with several tens of nanometers resolution.
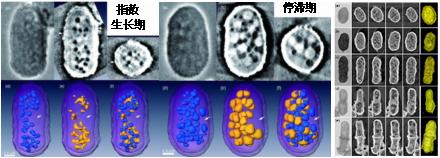
NSRL has built a zone plate based X-ray imaging beamline and station with spatial resolution better than 50 nm, and has carried out many works of the application with this nano-CT facility. In cell imaging, the fission yeast, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, was used for hard X-ray microscopy. A series of sample preparation processes including fixation, staining, dehydration and drying were applied first, then 2D radiographs are taken at 8 keV phase contrast mode. The images of fission yeast cells displayed sufficient contrast for examining cellular ultra-structures. By using nano-CT technique, subcellular structural organizations of whole cells were visualized in 3D at the resolution better than 100 nm. After segmentation and 3D rendering, the results clearly show the methodology of the whole cell and the organelles, such as cell wall, vacuole and mitochondria). Using quantitative analysis we can also obtain the information and the thickness of the cell wall and the specific parameters of some organelles, such as the shape, size, number and spatial distribution in the cell. The 3D structure of the cell can also be made as a video in different view, which more are easy and clear to observe the 3D structural of the cells.
Although there are some reports about the study of cell imaging using soft X-ray microscope, the application of the hard X-ray phase contrast imaging for cell imaging are rarely reported. Our studies of the yeast cells with hard X-ray nano-CT, including the sample preparation, experimental methods and results analysis, has been report in some international journals and conference proceedings, such as J. Microscopy. (2010), Anal. Bioanal. Chem. (2010) and XRM2010.
9.jpg
Back

