Nitrogen-Doped sp2-Hybridized Carbon as a Superior Catalyst for Selective Oxidation
The activation of saturated C-H bond, which is one of the most challenging projects in chemistry, is well known as the Holy Grail in chemistry. The direct oxidation of C-H bond is one important measure to activate C-H bond, which can directly convert the inert hydrocarbon to the active oxygen-containing compounds such as alcohols, aldehydes and carboxylic acids. However, harsh conditions such as high temperature, high pressure and strong acids were needed at present in the activation of C-H bond. Besides, precious metal catalyst is usually essential to the reactions. Therefore, in order to achieve the process of green chemistry, it is significant to develop a green catalytic system without precious metal catalyst and pollution for the oxidation of C-H.
Nano-carbon materials exhibit the ability to activate the C-H bond in high temperature. In addition, doped hetero atoms in nano-carbon materials can improve the catalytic activity of carbon materials. Ding Ma’s group in Peking University achieved the oxidation of saturated C-H bond in moderate conditions with nitrogen-doped sp2 carbon as catalyst and water as solvent. The catalytic activity of this carbon catalyst in oxidizing ethylbenzene to acetophenone is even comparable to that of noble metal catalyst ( ruthenium complex ) under the similar reaction conditions ( Conversion: 94.0 %, Yield: 80.4 % ). This catalytic system is active not only for the benzylic C-H bonds but also unactivated C-H bonds such as C-H bonds in cyclohexane and hexane. In order to clarify the why the metal-free nigtrgen-doped sp2 carbon perform excellent catalyst in the oxidation of saturated C-H bond, Prof. Ding Ma’s group collaborated with NSRL (National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, USTC) to research the reaction process. In the quasi-in-situ XAS research, it was found that that nitrogen atoms in carbon matrix stimulated the generation of reactive oxygen species ( C-O-O-H or C-O-C ) which can oxidize C-H bond. This result is important and instructive to determine the catalytic active sites in catalyst and the mechanism of the oxidation.
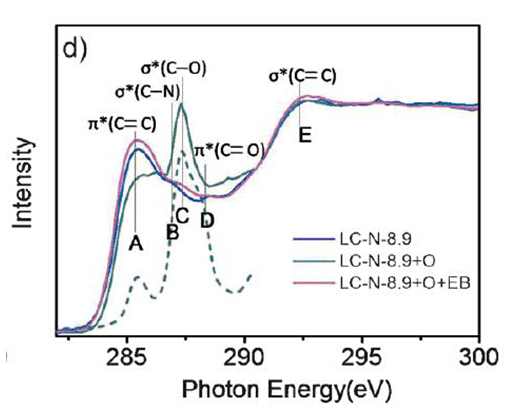
Figure 1. C K-edge XAS spectra of the processed nitrogen-doped carbon catalyst. ( note: LC-N-8.9 is nitrogen-doped carbocatalyst with 8.9 wt% content of nitrogen;LC-N-8.9+O is LC-N-8.9 processed by TBHP;LC-N-8.9+O+EB is LC-N-8.9+O processed by ethylbenzene for 10 hours )
QQ截图20141021162927.jpg
Back

